The need for Internet public policy in Togo
The International Institute for Sustainable Development recently published the outcome of a two-year study of Internet public policy participation in the West African nation of Togo. In summary, it finds that, technology growth has influenced urban centers, but has yet to make major in-roads in rural areas. Despite political and economic challenges, the Togolese embrace the opportunities that the Internet can offer, and many are ready to do business online. Broadband deployment, which stakeholders feel can contribute to their economic and social development, has been unaffordable by the poor population, of which over 60 per cent live below the national poverty line.
What to know about the outlook for greater Internet access in Togo:
- Mobile cellular uptake show growth from 6 to nearly 40 per 100 inhabitants from 2004 to 2010 (ITU, 2011).
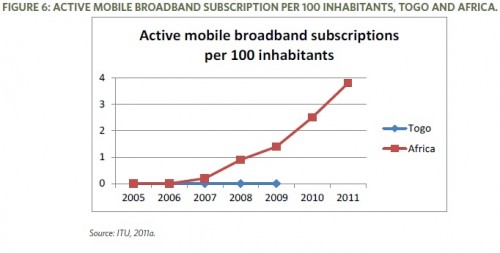
- 1 per 100 inhabitants live in a household with Internet access. Broadband remains largely unavailable.
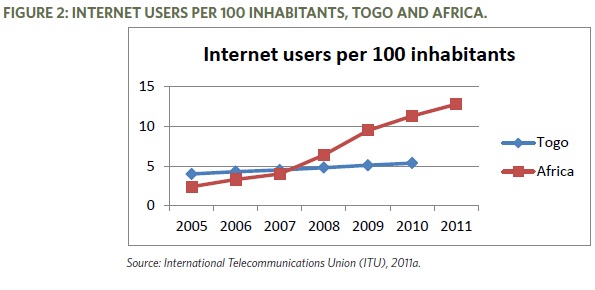
- There are approximately 324,000 Internet users, representing 5.4 per cent of the total population (ITU, 2011). The average for Africa is 12-13%.
- Two major Internet service companies provide access: Café Informatique (the largest) Togo Telecom (the incumbent). There are nearly 179 ISPs and cyber cafes in Lome.
- Consumers can pay up to 25,000 FCFA (US$50) for a 3 GB cap that allows between 8 and 20 hours of Web browsing in a 30-day window from Moov Togo (Moov, n.d.b), or 15,000 FCFA (US$30) for unlimited (undisclosed cap) bandwidth for Togocel for the same period (Togocel, 2012a). Such cost may be unaffordable to the almost 62% of the population living below the national poverty line (World Bank, 2012).
- The demand for broadband services from sectors such as education, agriculture, and health is yet to gain hold.
- A West African-wide survey, taken by stakeholders in Togo, was conducted in June 2010. 60% of all respondents were very concerned about the importance of access to and trust in doing business on the Internet. Over 85% of respondents agreed that governments and all stakeholders share the responsibility for the evolution of the Internet in Togo. Nearly all wanted a public forum on ICT.
- A survey on Internet governance was conducted in April 2011. Interestingly, 98% of respondents preferred a computer to a mobile device. Over 87% of respondents accessed the Internet from their office or cyber cafe. Only 5% of respondents say there is mobile broadband available in Togo or have experienced mobile broadband connectivity.
An opportunity exists for Togo to leverage the proliferation of mobile subscription to drive broadband deployment. More effort is required on the part of all stakeholders, particularly government and the private sector, for this to take place. An official national ICT policy (in the planning stage) should help.
Source: “Supporting Multistakeholder Internet Public Policy Dialogue in a Least Developed Country: The Togo Experience,” Ben Akoh, International Institute for Sustainable Development, July 2012.












 Twitter
Twitter Facebook
Facebook Pinterest
Pinterest