Report stresses need for African public, private, and social cooperation to build ICT ecosystem
Dalberg Global Development Advisors, with support from Google, surveyed more than 1,300 businesses in Senegal, Ghana, Kenya, and Nigeria as part of the April 2013 “Impact of the Internet in Africa” report. Interviews with a variety of experts gave further meaning to the data. The hope is that the information contained in this report can give policymakers the tools to build thriving internet ecosystems. The growth trajectory of ICT in Sub-Saharan Africa is on the right path, but countries still need to invest in core infrastructure and good usage conditions.
From the Executive Summary we can find the key points of the Dalberg report:
- Despite constituting 15% of the global population, only 6% of the world’s Internet users live in SSA.
- 70% of SME owners will hire new employees to leverage the internet as a means of growing business.
- At least in the four surveyed nations, new organizations are using the Internet in more complex ways than organizations that have been online for longer periods.
- Within the agriculture industry, access to information was listed as especially essential to business.
- mHealth and eHealth initiatives have existed for some time now, but most solutions are still in pilot stage.
- The education sector strongly values the internet but learning innovation outside the classroom needs better access to quality bandwidth.
- All businesses can benefit from an online presence (for marketing needs) even if online payment is not common.
- eCommerce is scarce in SSA, but mobile money is emerging in most nations and more than 60% of financial organizations see the Internet as essential.
- Social media use should lead to more advanced internet use in the future, especially in terms of citizen engagement.
- Now that first-time internet users are doing so via mobile, new ways of thinking about infrastructure requirements are needed.
- High speed broadband is needed to realize the benefits of cloud computing (for SMEs in particular).
Recommendations focus on cooperation among all parts of society, with the government as the primary driver:
- Public, private, and social sectors will need to set policy to build an ecosystem for innovation.
- Investment in infrastructure is needed to allow innovation to flourish. Affordability and awareness of solutions cannot be leapfrogged.
- Governments can play 3 primary roles: leadership (setting national ICT vision), governance (creation of legislation), and promotion of e-government services.
- A balance of market forces and healthy competition is needed in the private sector.
- The public sector should lead by example to support citizens’ entry to online.
Two key visuals:
The array of ICT solutions is impressive across all sectors:

Selected examples of Internet-enabled solutions driving impact on socioeconomic development. Click to enlarge. {Dalberg}
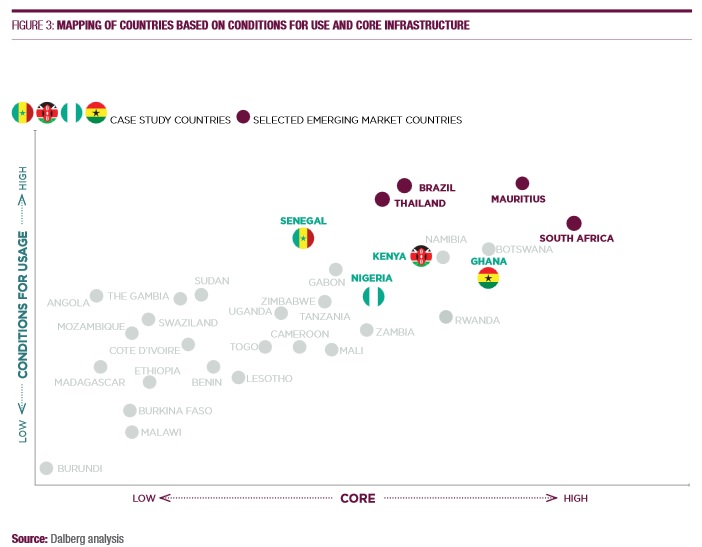
Conditions for use can only go so high without also strengthening core infrastructure. For example, no African country has a strong ICT core with low conditions for usage.
Read the full 102-page report to find detailed profiles of agriculture, health, education, SMEs, finance, energy, and governance.
Source: “Impact of the Internet in Africa: Establishing conditions for success and catalysing inclusive growth in Ghana, Kenya, Nigeria and Senegal,” Dalberg, April 2013, http://www.impactoftheinternet.com.












 Twitter
Twitter Facebook
Facebook Pinterest
Pinterest